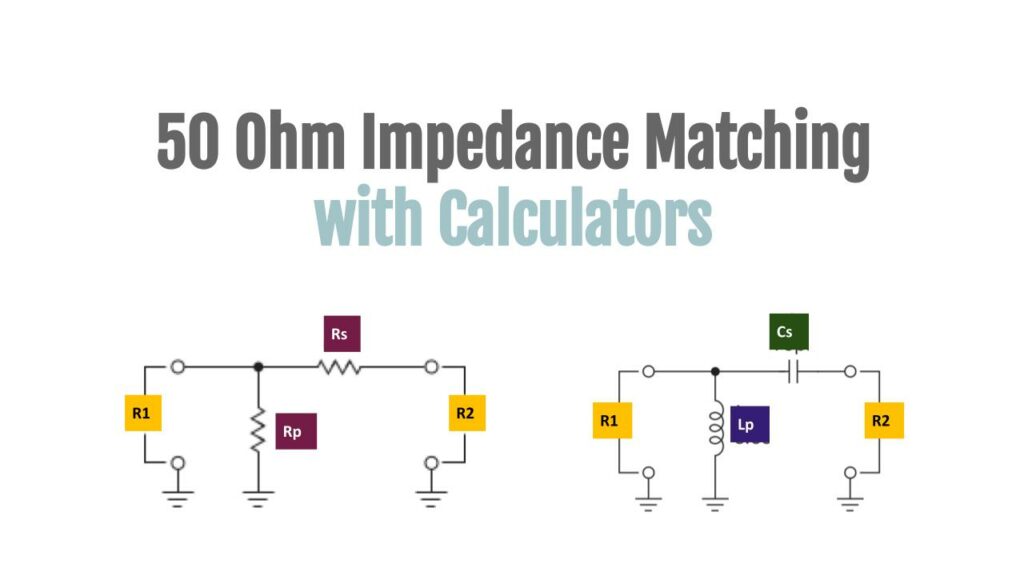
One Of The Best Info About Which Is Better, 50 Ohm Or 75

Jual Matching Impedance /Impedance Converter 75 Ohm To 50 Shopee
Decoding the Mystery
1. What's the Big Deal with Ohms, Anyway?
Ever wondered what those numbers, 50 ohm and 75 ohm, actually mean when you see them on cables and equipment? It's not just some random code! It refers to the impedance of the cable. Think of impedance as the resistance a cable offers to the flow of electrical signals, kinda like how a pipe resists the flow of water. Getting the right impedance match is super important for clear signal transmission. Mismatched impedance? That's a recipe for signal reflections, loss, and all sorts of undesirable electronic gremlins.
So, why two common standards like 50 ohm and 75 ohm? It boils down to different application needs. Each impedance value is optimized for specific types of signals and frequencies. One isn't inherently "better" than the other; it's about choosing the right tool for the job. Imagine trying to use a screwdriver to hammer in a nail — technically, you could do it, but it's far from ideal! That's similar to mismatching impedance.
This difference might seem subtle, but trust me, it matters! It can be the difference between crystal-clear data transmission and a frustrating, glitchy experience. We'll delve deeper into where each type shines, so you can confidently choose the right cable for your setup.
Let's jump in to explore the world of impedance and how it impacts your tech life. Prepare to have your mind a little bit ohmed. (Sorry, I had to!)
50 Ohm
2. Where Does 50 Ohm Shine?
50 ohm cables are the workhorses of radio frequency (RF) power transmission. Think about applications like two-way radios, ham radio setups, and even Wi-Fi antennas. The design of 50 ohm cables prioritizes power handling and minimizing signal loss over longer distances. They're built to take a beating and keep the signal strong.
Why 50 ohms? There's a bit of historical reasoning behind it, dating back to early radio engineering. Engineers discovered that 50 ohms offered a sweet spot, balancing power handling and low attenuation (signal loss). While other impedance values might theoretically be slightly better in one area or another, 50 ohms provided the best all-around performance for many RF applications. Consider it a golden compromise!
So, if you are setting up a powerful WiFi system, a radio transceiver, or a communication link, the 50 ohm impedance is really appropriate. They're robust and handle the power with care.
Another really important application is test and measurement instruments. Think spectrum analyzers, signal generators, and network analyzers. Because of the need for accurate signal handling, 50 ohm is used. In this sector, stability of impedance is really important!

Ohm Resistance Chart
75 Ohm
3. 75 Ohm — Picture Perfect Performance
75 ohm cables are the go-to choice for video signals. You'll find them in your TV antennas, cable boxes, satellite receivers, and CCTV systems. The magic of 75 ohm lies in its ability to efficiently transmit video signals with minimal signal reflection, ensuring a clear and crisp picture on your screen.
Why 75 ohms for video? Well, the characteristics of video signals lend themselves particularly well to this impedance. It's optimized to minimize signal loss and reflections over the frequencies used for video transmission, especially over coaxial cables. Back in the day, cable TV companies standardized on 75 ohms, and it became the industry standard. And, hey, who are we to argue with a clear picture?
So, if you're connecting your TV to an antenna, cable box, or satellite receiver, you'll almost certainly be using 75 ohm cables. Using the wrong impedance here could lead to ghosting, blurry images, or even a complete loss of signal. Nobody wants that when they're trying to binge-watch their favorite show!
A critical point of note is that the impedance also affects the construction of the coax cable. A 75 ohm coax will have differing physical dimensions than a 50 ohm cable to achieve that impedance. Don't just try to eyeball it!

50 Ohm Vs 75 Which Is Better For Your Application? RayPCB
Mixing and Matching
4. Playing Matchmaker
This is where things get a little tricky. In general, you want to avoid mixing 50 ohm and 75 ohm components in your system, especially in critical signal paths. Mismatched impedance can lead to signal reflections, which cause signal loss, distortion, and reduced performance. Imagine trying to fit a square peg in a round hole — it's not going to end well!
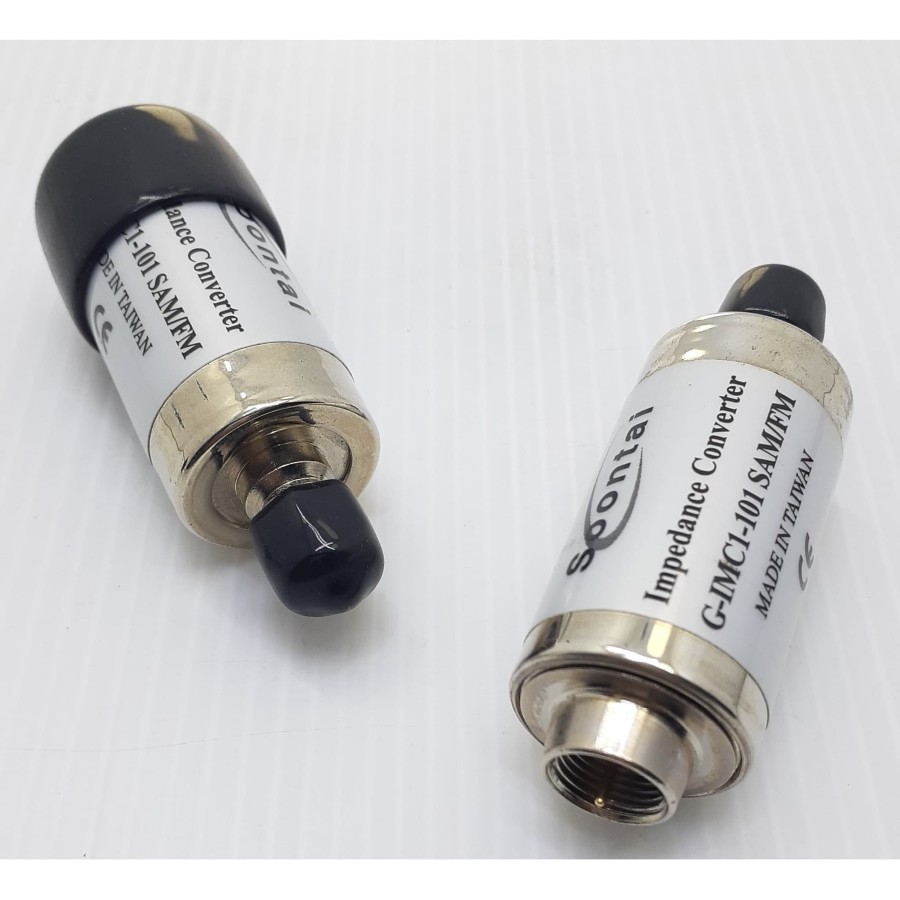
There are some exceptions, but these typically involve using impedance matching devices called "matching networks" or "baluns." These devices are designed to convert between different impedance levels while minimizing signal loss and reflections. However, using these devices adds complexity and can introduce some signal degradation, so it's best to avoid impedance mismatches whenever possible.
For example, connecting a 50-ohm antenna to a 75-ohm cable run and into a 75-ohm receiver is likely to cause signal loss and an increase in standing wave ratio (SWR), potentially harming the transmitter. It can be an expensive mistake!
The rule of thumb is "stick to what the manufacturer requires." If the device is meant to operate at 75 ohms, use 75 ohm cables and devices. Mixing impedances is almost always the wrong choice. Unless you know exactly what you're doing with specialized impedance matching equipment, avoid it at all costs.

Making the Right Choice
5. Choosing the Correct Impedance for Your Application
Choosing between 50 ohm and 75 ohm doesn't have to be a daunting task. Here's a simple guide to help you make the right choice:
- Radio Communication: If you're working with radios, antennas, or transmitters, 50 ohm is almost always the way to go.
- Video Signals: For connecting TVs, cable boxes, satellite receivers, or CCTV systems, 75 ohm is the standard.
- Read the Manual! When in doubt, consult the equipment's user manual or manufacturer's specifications. They'll usually specify the correct impedance.
- Don't Guess! Avoid guessing or assuming. Using the wrong impedance can negatively impact performance and potentially damage equipment.
Think of it like this: using the right impedance is like using the correct type of fuel for your car. Putting diesel in a gasoline engine (or vice-versa) is a recipe for disaster. Similarly, using the wrong impedance can cause performance problems and even damage your equipment. A little bit of research can save you a lot of headaches in the long run!
In summary, while both 50 ohm and 75 ohm cables are useful, it is critical to use the correct type for your specific application to ensure optimal signal integrity and prevent damage. Selecting the correct impedance can drastically affect the performance of electronic components.